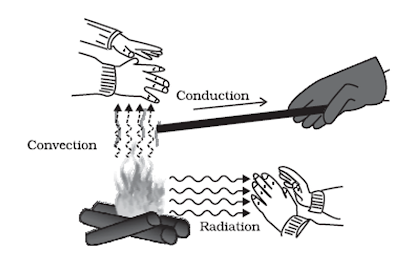
Heat is a disordered form of energy and it transfers from one body to other over temperature difference. There are three basic ways of heat transfer namely conduction ,convection and readiation.
Conduction happens through solids where no particle of medium is permanently displaced and heat transfer takes place because of vibration of particles about mean position.During the vibration particles transfers heat energy to next particles and so on.
In the case of convection each particle of the medium gets a permanent displacement and transfers the heat energy. Convection happens through liquids and gases. This is a bit quicker than conduction.
Radiation does not requires materiel medium for propagation and it happens even through vacuum. It is the quickest way of transfer of heat energy and happens with velocity of light.
 Conduction :
Conduction :
Gases are poor thermal conductors while liquids have conductivities intermediate between solids and gases.
Let us consider a metallic bar of length L and uniform cross section A with its two ends maintained at different temperatures. Let us assume the ideal condition that the sides of the bar are fully insulated so that no heat is exchanged between the sides and the surroundings.

After sometime, a steady state is reached; the temperature of the bar decreases uniformly with distance from TC to TD; (TC>TD). The reservoir at C supplies heat at a constant rate, which transfers through the bar and is given out at the same rate to the reservoir at D. The rate of flow of heat (or heat current) H is proportional to the temperature difference (TC – TD) and the area of cross section A and is inversely proportional to the length L :
H = KA [Tc –TD] / L
The constant of proportionality K is called the thermal conductivity of the material. The greater the value of K for a material, the more rapidly will it conduct heat.
Other useful topics in physics
Heat and Temperature
Change of State
Surface energy and tension
Viscosity
Dynamic lift
Conduction happens through solids where no particle of medium is permanently displaced and heat transfer takes place because of vibration of particles about mean position.During the vibration particles transfers heat energy to next particles and so on.
In the case of convection each particle of the medium gets a permanent displacement and transfers the heat energy. Convection happens through liquids and gases. This is a bit quicker than conduction.
Radiation does not requires materiel medium for propagation and it happens even through vacuum. It is the quickest way of transfer of heat energy and happens with velocity of light.
 Conduction :
Conduction :Gases are poor thermal conductors while liquids have conductivities intermediate between solids and gases.
Let us consider a metallic bar of length L and uniform cross section A with its two ends maintained at different temperatures. Let us assume the ideal condition that the sides of the bar are fully insulated so that no heat is exchanged between the sides and the surroundings.

After sometime, a steady state is reached; the temperature of the bar decreases uniformly with distance from TC to TD; (TC>TD). The reservoir at C supplies heat at a constant rate, which transfers through the bar and is given out at the same rate to the reservoir at D. The rate of flow of heat (or heat current) H is proportional to the temperature difference (TC – TD) and the area of cross section A and is inversely proportional to the length L :
H = KA [Tc –TD] / L
The constant of proportionality K is called the thermal conductivity of the material. The greater the value of K for a material, the more rapidly will it conduct heat.
Other useful topics in physics
Heat and Temperature
Change of State
Surface energy and tension
Viscosity
Dynamic lift
No comments:
Post a Comment